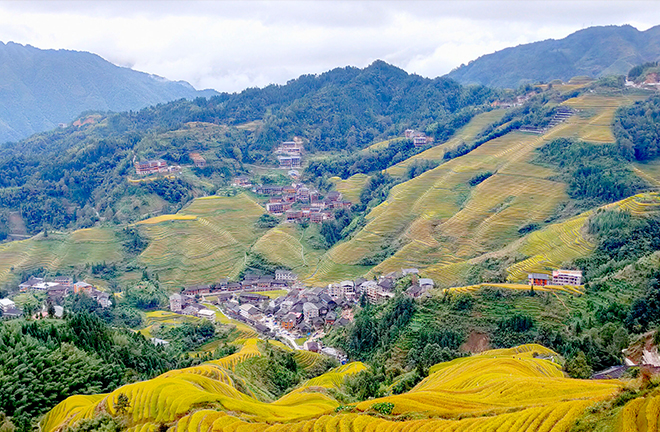
Known as the most beautiful terrace in China, Longji Rice Terraces in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region are developed jointly by local governments, companies, and villagers under a reasonable benefit distribution mechanism, which effectively ensures the maintenance of the agricultural landscape by multi-stakeholders. Photo: Yang Xue/CSST
Rural tourism has played an irreplaceable role in rural vitalization strategy. To name a few, rural tourism helps promote the integration of primary, secondary and tertiary industries in rural areas, optimize and upgrade the rural industrial structure, and achieve targeted poverty alleviation due to its advantages in integration, strong correlation, and wide reach. The development of rural tourism is conducive to bringing more factors and resources to rural areas, in order to achieve rural vitalization, agricultural, and rural modernization now that China completed its mission to eradicate extreme poverty in 2020.
The high-quality development of rural tourism requires mass participation from the government, enterprises, villagers, and tourists, to form a value co-creation mechanism. Within this collaborative effort, the role of private enterprises cannot be underestimated. By the end of 2019, the number of private enterprises in China had exceeded 30 million, and their market influence has become increasingly prominent. By August 2020, 82% of the 1,542 national leading enterprises identified by eight government departments, including the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, were private enterprises, while more than 90% of the country’s 90,000 leading enterprises above the county level were also private enterprises.
As the backbone of rural tourism development, private enterprises should enhance their role in the comprehensive planning and coordination of tourism resources and strive to open up new industrial patterns under the joint policy and market push.
Activating rural tourism resources
Private enterprises are the bridge between rural tourism resources and the market, as tourist products connect villagers and tourists. The prominent feature of rural tourism is that visitors travel to the countryside, immerse in rural landscapes, get a taste of rural life, and interact with villagers. Visitor consumption is the process through which tourist products and services enter the market.
For private enterprises, in addition to the supply of tourism products and services, they take advantage of their market-oriented operation mechanisms and professional platform technologies to create innovative rural tourism development through enterprise capital, industrial models, marketing and brand building, which promotes the transformation of rural tourism resource advantages into industrial advantages.
In this process, private enterprise guidelines in cost controls and market operations improve the supply and demand balance of rural tourism, and help foster a healthy ecosystem for rural tourism development.
By coordinating between villagers and tourists, and unifying enterprise resources, government policies and market elements, private enterprises fully explore the value of rural tourism and maximize comprehensive benefits. The flat organizational structure and flexible operation of private enterprises allow them to respond quickly to tourists’ needs, industrial environments and policy guides, to activate a variety of rural resources according to local conditions, and meet the diversified market needs.
The flexibility and autonomy of private enterprises in benefit distribution enables them to share the gains of rural tourism development with villagers in a timely manner. Private enterprises are mainly small and medium-sized enterprises, which allows them to closely contact and exchange with villagers to form a value community. At present, many private enterprises establish farmer cooperatives, joint ventures, and other entities, which absorbs rural surplus labor and brings villagers into a common interest network, thus generating a common prosperity for rural communities.
Integration of the three industries
The natural environment, farmhouses, local rules and customs, and traditional ways of life such as crop-growing, fishing, or forestry are all potential resources in rural tourism. In reality, due to the lack of awareness of resource development and transformation, many villages with rich tourism resources are left idle or become abandoned through mergers and relocations. Some folk customs and intangible cultural heritage that were not included on the protection list have gradually vanished amid drastic social changes.
In this regard, private enterprises realize endogenous and bottom-up development in terms of cultural inheritance, heritage protection, and ecological construction. On this basis, they facilitate the flow of factors between urban and rural areas and help form a beneficial interactive cycle in which talent, capital, technology, information, and other resources gather in the countryside.
In the meantime, rural tourism integrates the primary, secondary, and tertiary industries in rural areas, and enhances the agglomeration of rural industries, laying a solid industrial foundation for rural vitalization. For example, Liangquan Ideal Village, located in Laoshan District, Qingdao City, is a successful case where private enterprise participated in rural tourism and promoted the integration of the three industries in rural areas. Chinese cultural travel operator Xband Club designs, plans, and builds a charming Liangquan Village that integrates idle rural housing compounds, modern agriculture, and leisure tourism such as vegetable planting, processing agricultural products, sightseeing, fruit and vegetable picking activities, and the production of creative arts. Within a short period of time, the decaying village was transformed into a benchmark rural tourism spot, opening up a new rural governance path featuring ecological revitalization and green empowerment.
Policy stimulus
As of today, private enterprises have increasingly become the driving force for rural tourism development. Specializing in rural tourism, private enterprises have continually upgraded the industrial chain, supply chain, and consumption chain, while improving their professionalism and brand in the market. In the future, through regional cooperation on projects, the reform and innovation capacity of private enterprises should be further enhanced, and the coordinated development of different enterprises should reorganize, so as to expand the influence of private enterprises in rural tourism and optimize the market layout.
At the same time, private enterprises should take advantage of policy stimulus and increase their share of rural tourism development. In 2014, the General Office of the State Council issued a document which promoted the reform and development of tourism. The document explicitly stated for the first time that credit support would be increased for small and micro tourism enterprises and rural tourism initiatives. Since then, the government has issued policies related to rural tourism development almost every year, and there is an abundance of support for private enterprises. In September 2020, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs said that it would encourage and support private enterprise investment in new businesses in rural areas, boosting the confidence of private enterprises to participate in the development of rural tourism.
Diverse values of rural tourism
Private enterprises have deeply engaged in rural tourism development through investment, operation, and management. While generating economic benefits, they should also work on maintaining the sustainable development of rural areas. As Chinese President Xi Jinping pointed out: “Lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets.” Private enterprises rely on rural resources to create wealth. Through this process they also see spillover effects in rural tourism, which directly or indirectly promotes agriculture, agricultural product processing, and other service industries. In this light, private enterprises could better coordinate and achieve synergy in different industries.
Second, the ecological environment’s quality directly determines the success or failure of rural tourism’s development. However, due to limitations including geographical location, infrastructure, technical means, and other conditions, rural areas’ ecological environments have certain sensitivities. Therefore, private enterprises should strive to form an ecological protection network by fostering citizen consciousness among villagers, stressing the protection of ecological environments in rural development, and supervising and regulating tourist behaviors.
Finally, folk customs and farming cultures are the most valuable cultural resources in rural areas, and also the core elements which attract private enterprises to participate in rural tourism development. Going forward, private enterprises should dig deeper into agricultural, rural, and regional culture, and explore the optimal development path for each individual village. In operating businesses, private enterprises may also help smooth the relationship between villagers and tourists, blend tourists into the rural culture, shape the new rural culture of modern society, and enhance the indigenous power of rural development.
Wang Xiuwei and Li Xiaojun are from the Research Base of National Culture and Tourism at the Ocean University of China.
Edited by YANG XUE