Academic approaches to qualify craftsmanship
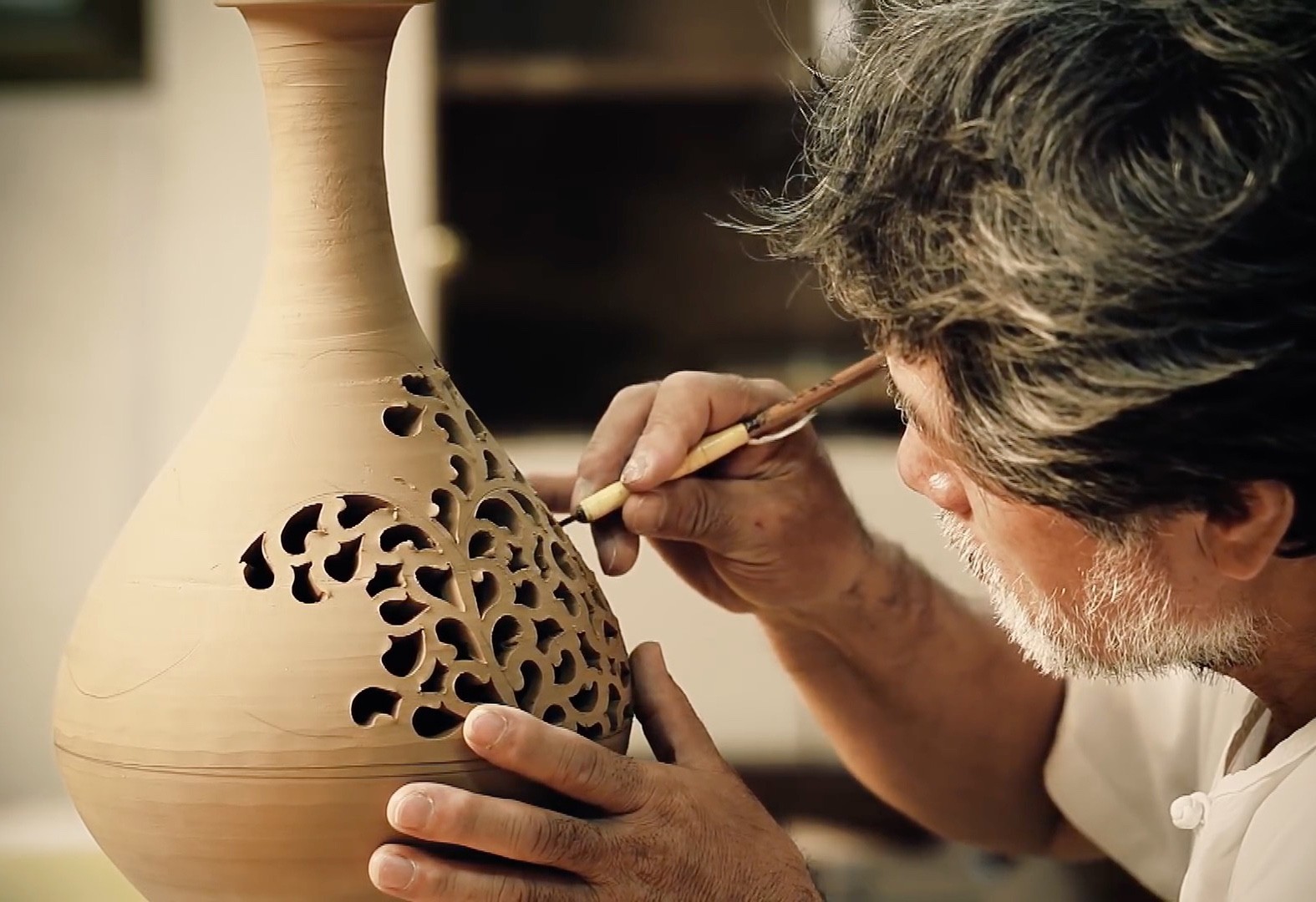

The spirit of craftsmanship emphasized today is not the continuation of traditional handicraft labor, but rather a value system that advocates the spirit of obeying contracts, responsibility and the pursuit of quality.
The spirit of quality lies in craftsmanship. The “spirit of craftsmanship” was introduced by Premier Li Keqiang in the report on the work of the government in 2016, and the 2017 report again brought forth “the culture of craftsmanship.” Issues related to “craftsmanship” have become a concern relating to the nation’s top-level design and an essential social demand. “Big country manufacturing” requires “great craftsmen”, and “great craftsmen” cannot exist without the spirit of craftsmanship.
Value system
The spirit of craftsmanship is the value system formed in the long history of complex labor. Due to the integrity of the design, production and sales of handicrafts, as well as the participation of craftsmen in the whole production process, craftsmen must be fully responsible for the final product, which nurtured their ultimate pursuit of quality and high sense of responsibility for users.
He Renke, dean of the School of Design at Hunan University, said the spirit of craftsmanship we emphasize today is not the continuation of traditional handicraft labor, but rather a value system that advocates the spirit of obeying contracts, responsibility and the pursuit of quality.
Zou Qichang, a professor from the College of Design and Innovation at Tongji University, chief expert of the National Social Sciences Fund Major Project “Innovation Research on Chinese Craftsmen Culture System and Inheritance,” said the spirit of craftsmanship could be interpreted from “practical” and “transcendental” dimensions. The practical dimension is characterized by “skillfulness” (technical principles), “decoration” (artistic principles), “rules” (codes of conduct), and “harmony” (ecological principles). The integration of the four basic elements nurtures the materialization of the spirit of craftsmanship. For the transcendental dimension, the spirit of craftsmanship refers to a way of living, outlook on life and attitude toward work. Therefore, we need the spirit of craftsmanship to achieve values that will help us to improve our work and better meet material and spiritual demands.
Cultural atmosphere
Fang Xiaofeng, a professor from the Academy of Arts and Design at Tsinghua University, pointed out that the spirit of craftsmanship, which advocates “slowness and delicacy,” is not necessarily out of place in an industrial society that emphasizes “speed and extensiveness.” During the period of industrialization, machines on a large scale took the place of manpower, but people are still the most critical factor in production.
Some scholars have argued that “craftsmen” refers to any kind of worker, including national administrators at all levels, scientists, technicians, designers, artists in various fields. Anyone who is highly responsible and does their work well is a “craftsman.” Therefore, “craftsmen” is a concept unified in historical significance and synchronicity. The core value of the spirit of craftsmanship lies in diversity, pluralism and innovation.
Zou said the spirit of craftsmanship is not rare. What is currently lacking are mechanisms as well as cultures that interact with these mechanisms. Therefore, the restoration of the spirit of craftsmanship requires the construction of a “craftsman culture” system on academic level, while conducting systematic research and practice in order to promote the modern transformation of the traditional spirit of craftsmanship that will lay a solid foundation for an upgrade of national and social development. This is an academic and social issue closely tied to national development. The three natures of the spirit of craftsmanship are interactively constructive. The interaction between the three aspects can form an innovative “craftsman society” led by the spirit of craftsmanship and founded on the “craftsman culture.”
Big country manufacturing
Fang said shaping the “big country manufacturing” image requires the integration of resources in economic globalization on the basis of the latest technology. It is necessary to establish a market-driven quality management system with design as the pilot and brand as the core. The Internet, as well as the Internet of Things, is needed to build mutual trust between enterprises and consumers, in order to enhance consumer experience and loyalty.
In addition, the establishment of “big country manufacturing” cannot rely on the cultivation of cutting-edge technologies. “Big country” here refers not to the national territorial area or population scale, but to industrial or professional influence. “Big country manufacturing” needs comprehensive and consistent promotion for technical and production research and development. The machines are only manufacturers, while the key part is still human and their particular ways of thinking.
SU PEI is a reporter at the Chinese Social Sciences Today.